Collecting and Managing Quality Data with Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems CSGB.NET

INTRODUCTION
When the ISG-SIS® project was started in 2014, it was clearly visible that activities carried out in the field of occupational health and safety in Türkiye had a structural problem. OHS data produced in workplaces was being kept through different software, different formats, and systems that couldn't communicate with each other, making effective management in the field difficult and preventing the creation of reliable and comparable statistics nationwide.
While developing ISG-SIS®, the fundamental awareness was this: Occupational health and safety processes, just like in health services, can and should be managed under a central structure, with a common data language and standard communication architecture. The digital health ecosystem created within the Ministry of Health over the years, known today as e-Nabız, clearly demonstrates the applicability of this approach. Just as all public and private health institutions are connected online to the Ministry of Health, it is possible to establish a similar digital integration between the Ministry of Labor and Social Security and workplaces.
In line with this vision, ISG-SIS® has been designed to ensure that occupational health and safety activities flow from the field toward a central structure in a standard, measurable, and verifiable manner. The main objective of the project is to define all OHS activities carried out in workplaces through a common data model, to automatically collect this data through software systems used in the field, and to transform it into meaningful statistics on a central platform.
ISG-SIS® has been considered not only as a software solution but also as a strategic public infrastructure approach that increases the effectiveness of regulatory implementations, reduces informality, and bases policy production on data. The architectural and methodological approach developed in this context was shared as a poster presentation at the 7th International Occupational Health and Safety Conference held at Haliç Congress Center on May 5-7, 2014; and was conveyed to relevant stakeholders, especially officials from the Ministry of Labor and Social Security Occupational Health and Safety General Directorate, at various seminars, congresses, and fairs.
The basic approach of ISG-SIS® is to create a structure where software used in the field communicates directly and securely with the central system within the Ministry of Labor and Social Security, instead of human-oriented manual reporting processes. Thus, the aim is not only to record data produced in the field of occupational health and safety but also to make it comparable, analyzable, and suitable for policy development nationwide.
In this article; the Common Data Model developed within the scope of the ISG-SIS® project, communication architecture, minimum data sets, accreditation approach, and concrete benefits provided for all relevant actors are discussed in detail.
CSGB.NET PROJECT DETAILS
Summary
Currently, data that would be useful for creating statistics on occupational health and safety cannot be collected in our country. Although there are various reasons for this situation, a common data model needs to be created in order to establish a common language through cooperation between the relevant ministry and the private sector.
Subsequently, all occupational health and safety software needs to be made compatible with this common data model. After this process, which can also mean accreditation for all actors in the relevant field, it will be possible to collect field data compatible with the common data model through a central system by the ministry and convert it into statistics. Thus, it will become possible for occupational health and safety policies in our country to be based on statistical data.
National Occupational Health and Safety Policy Document - III and Action Plan (2014-2018) References
Goal 2: Development of occupational accident and occupational disease statistics and registration system (Page 29)
The only source we can access occupational health and safety statistics in our country is SGK statistics. According to this data, in 2013, 191,389 reported occupational accidents and 371 occupational disease cases approved by the institutional health board occurred in Türkiye, and a total of 1,360 people lost their lives as a result of occupational accidents. There are no fatal occupational disease cases. According to these figures, approximately 524 insured workers have occupational accidents daily in Türkiye, 4 people lose their lives as a result of occupational accidents, and 5 people become disabled as a result of occupational accidents. In addition to these figures, losses as a result of occupational diseases that are not reflected in SGK statistics should also be taken into account. These statistics show that there are problems in the detection and reporting of occupational accidents and diseases, and it is aimed to develop statistics and registration systems to eliminate these problems.
Goal 4.3: Electronic transmission of occupational disease data collected at university hospitals to the Ministry of Health (Page 34)
By transmitting the occupational disease data collected at university hospitals to the Ministry of Health, complete and accurate information will be ensured through parallel control of the data.
Goal 6: Spreading occupational health and safety culture in society (Page 38)
With the Occupational Health and Safety Law No. 6331 and its sub-regulations, legislative work on this subject has been completed and updates are being made in line with changing needs. However, the establishment of health and safety culture in society is possible not only with legislative regulations but also by changing the behavior of people in society. In this direction, increasing activities to be carried out for the purpose of creating "Occupational Health and Safety Culture" will increase the awareness level of society.
6.8. Conducting awareness activities on the effects of OHS practices on productivity (Page 42)
In order to encourage employers regarding OHS practices, the effects of OHS practices on productivity in workplaces will be researched and the data obtained will be shared with employers. The visible positive results of reducing accidents, workday losses, and indirectly production losses through investments made by businesses in OHS and increasing employee motivation will be clarified by studies to be conducted on how they are reflected in business expenses.
Goal 7: Making MYK Vocational Qualification Certificates mandatory in hazardous and very hazardous jobs (Page 42)
In order to make MYK Vocational Qualification Certificates mandatory in hazardous and very hazardous jobs in line with the goal of improving the OHS environment by employing qualified workforce with MYK Vocational Qualification Certificates, reducing occupational accidents, and increasing productivity, necessary legislative changes need to be made. This obligation will cover the professions specified in the communiqués to be issued by the Ministry of Labor and Social Security.
1. What is the Common Data Model (CDM)?
It is a template that expresses what minimum data should be included in the data structure that will express any OHS activity carried out in the workplace. The data in the relevant template is expected to have the following characteristics:
- a. Should be suitable for creating statistics
- b. Numerical equivalents of definition data should be used
- c. Numerical and verbal equivalents of definition data should be centralized
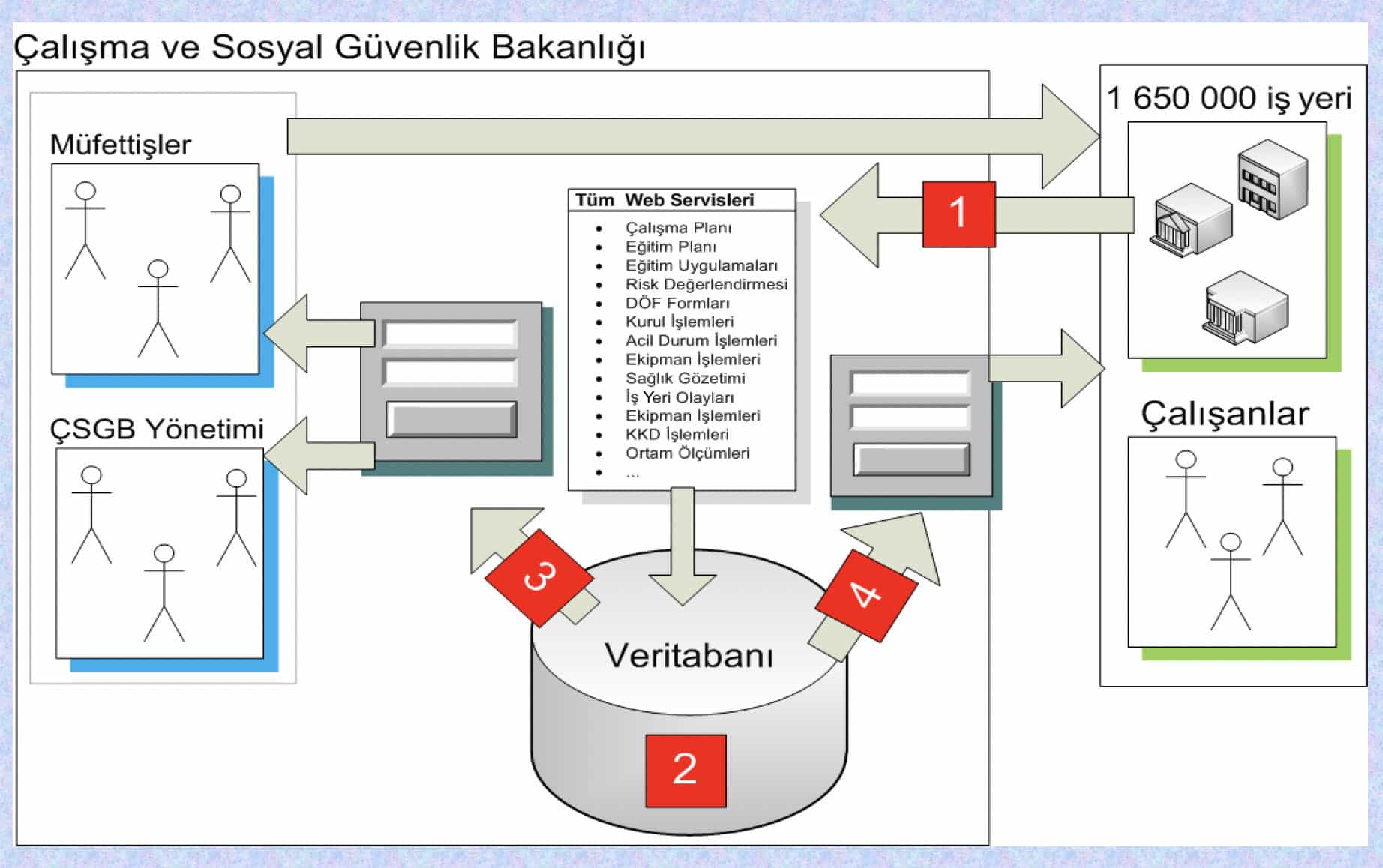
2. Communication Architecture
There will be various actors who will use the specified data model, and all relevant actors will be in communication with the Ministry of Labor and Social Security through the software systems they use within the specified rules. In other words, it will be a system where field software talks to the software system at the Ministry of Labor and Social Security center, not humans. This communication and data exchange platform to be provided by software technology will be continuously developed according to field demands and ministry needs.
Almost all of the manual work likely to be done by humans will work automatically according to scheduled rules. For example, warning a workplace that is doing incomplete work in terms of OHS will be done automatically through the system.
3. Main Topics
The main topics can be expressed item by item as follows:
- 3.1 Workplace
- 3.2 Work Plan
- 3.3 Training Plan
- 3.4 Training Implementation
- 3.5 Risk Assessment
- 3.6 Corrective Preventive Action
- 3.7 OHS Committee
- 3.8 OHS Committee Meetings
- 3.9 Emergency Planning
- 3.10 Emergency Scenarios
- 3.11 Emergency Drills
- 3.12 Equipment Inventory
- 3.13 Equipment Periodic Maintenance
- 3.14 Equipment Periodic Inspections
- 3.15 Chemical Inventory
- 3.16 Personal Protective Equipment Inventory
- 3.17 Examinations
- 3.18 Workplace Incidents (Near Miss, Property Damage Only, Occupational Accident, Occupational Disease)
- 3.19 Environmental Measurements
4. Common Minimum Data Sets
Common minimum data sets for main topics can be expressed as follows. All data sets can be expanded over time as needed.
WORK PLAN
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
WORK_PLAN_DATE
WORK_PLAN_NAME
WORK_PLAN_RESPONSIBLES (NAME, SURNAME, TC_ID_NO)
WORK_PLAN_ACTIVITIES (DATE, ACTIVITY, COMPLETION_STATUS)
TRAINING PLAN
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
TRAINING_PLAN_DATE
TRAINING_PLAN_NAME
TRAINING_PLAN_RESPONSIBLES (NAME, SURNAME, TC_ID_NO)
TRAINING_PLAN_ACTIVITIES (DATE, ACTIVITY, COMPLETION_STATUS)
TRAINING
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
TRAINING_DATE
TRAININGS (TRAINER, TRAINING_DURATION, THEORETICAL/PRACTICAL)
PARTICIPANTS (NAME, SURNAME, TC_ID_NO)
RISK ASSESSMENT
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
RA_DATE
RESPONSIBLES (NAME, SURNAME, TC_ID_NO)
RA_METHOD
RESULT_INFORMATION
CAP (Corrective Action Plan)
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
CAP_OPENING_DATE
DEADLINE_DATE
RESPONSIBLES (NAME, SURNAME, TC_ID_NO)
STATUS (OPEN, CLOSED)
ACTIVITIES
OHS COMMITTEE
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
CREATION_DATE
MEMBERS (NAME, SURNAME, TC_ID_NO, ROLE, TASK)
OHS COMMITTEE MEETINGS
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
OHS_COMMITTEE_CGSB_NO
MEETING_DATE
PARTICIPANTS (NAME, SURNAME, TC_ID_NO, ROLE, TASK)
DECISIONS (VOTING_RESULTS, DECISION)
EMERGENCY PLAN
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
EP_DATE
TEAMS (NAME, SURNAME, TC_ID_NO, ROLE, TASK)
EMERGENCY SCENARIOS
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
EMERGENCY_PLAN_CSGB_NO
SCENARIO_CONTENT
EMERGENCY DRILLS
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
EMERGENCY_SCENARIO_CSGB_NO
DRILL_CONTENT
EQUIPMENT INVENTORY
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
EQUIPMENT_TYPE (according to definitions to be determined by Ministry of Labor and Social Security)
EQUIPMENT_NAME
MANUFACTURING_DATE
EXPIRY_DATE
START_OF_USE_DATE
HAS_PERIODIC_MAINTENANCE
LAST_PERIODIC_MAINTENANCE_DATE
HAS_PERIODIC_INSPECTION
LAST_PERIODIC_INSPECTION_DATE
EQUIPMENT PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
EQUIPMENT_CSGB_NO
MAINTENANCE_DATE
MAINTENANCE_PROVIDER_INFO (COMPANY, NAME, SURNAME)
MAINTENANCE_RESULT (according to definitions to be determined by Ministry of Labor and Social Security)
EQUIPMENT PERIODIC INSPECTION
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
EQUIPMENT_CSGB_NO
INSPECTION_DATE
INSPECTION_PROVIDER_INFO (COMPANY, NAME, SURNAME)
INSPECTION_RESULT (according to definitions to be determined by Ministry of Labor and Social Security)
CHEMICAL INVENTORY
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
CHEMICAL_TYPE (according to definitions to be determined by Ministry of Labor and Social Security)
CHEMICAL_NAME
PPE INVENTORY
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
PPE_TYPE (according to definitions to be determined by Ministry of Labor and Social Security)
PPE_NAME
EXAMINATION
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
EXAMINATION_DATE
EMPLOYEE (NAME, SURNAME, TC_ID_NO)
DIAGNOSES (icd10 codes)
TESTS (according to definitions to be determined by Ministry of Labor and Social Security)
EXAMINATION_RESULT
WORKPLACE_INCIDENT
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
INCIDENT_TYPE (according to definitions to be determined by Ministry of Labor and Social Security)
INCIDENT_CONTENT
ENVIRONMENTAL MEASUREMENT
TEXT
WORKPLACE_CSGB_NO
MEASUREMENT_TYPE (according to definitions to be determined by Ministry of Labor and Social Security)
MEASUREMENT_CONTENT
5. Accreditation
Collecting data according to minimum common data set criteria in the field of occupational health and safety and being able to send it to the ministry through a central system will mean accreditation for all OHS actors in terms of speaking the same language. The steps of this process are as follows:
- A workplace that collects data with minimum data sets and sends it to the ministry will have passed the first stage of accreditation.
- The software company that will provide this digital integration between the workplace and the Ministry of Labor and Social Security will also have passed the first stage of accreditation.
6. Conclusion
Working according to a common data model will have concrete benefits for every actor in the OHS ecosystem:
6.1 Advantages for Ministry of Labor and Social Security
- All types of OHS operations of all workplaces in the country will be recorded.
- All types of OHS data from all workplaces in the country will be accessible instantly.
- It will provide great benefit in detecting and preventing informality.
- Compliance of all workplaces with determined standards in all relevant matters will be guaranteed.
- Employers' full compliance with OHS legislation will be ensured.
- Significant reduction of SGK expenses arising from occupational accidents and diseases will be achieved.
- Mutual data and information exchange with other relevant ministries will be possible.
- These quality statistics to be created will guide and develop the country's Ministry of Labor and Social Security policies and vision.
- Türkiye's reputation in OHS in the international arena will increase.
- Direct contribution to the country's economy will be made by increasing employee productivity.
6.2 Advantages for Workplace (Employer)
- It will make it easier for OHS policies in workplaces to be sustainable.
- A workplace with a better OHS report card will be able to benefit from preferability advantages. In addition, various incentives may also be provided by the state to workplaces with good OHS report cards.
- Employer-employee relations will be elevated to a healthier, safer, and more respectable level.
6.3 Advantages for Employee
- An employee working in a workplace that conducts OHS processes in accordance with legislation being away from occupational accidents and diseases will have a positive impact on the employee and the employee's family.
- With the ministry's approval, an employee will be able to easily access the OHS report card of a workplace they are about to start working at.
7. Cost Analysis
It will be determined according to the project development period and the number of technical personnel who will work in this process.
Digitize Your OHS Processes
Discover our comprehensive software solutions that collect quality data and are fully compatible with Ministry integration with ISG-SIS®.
Explore ISG-SIS®Contact Us
Our expert team is ready to help you get detailed information about your projects or request a demo.
Go to Contact Page